

The word Boer is from the Dutch word for "Farmer", the Boer's themselves were of Dutch, German, French origin first settled by the Dutch East India Company in 1648. The Company ran the Colony for its own monetary gain through the latter half of the 17th and the whole of the 18th century, troubles arose between the colonists and the administration of the Dutch East India Company who were extremely despotic. The Colonists who had hoped to escape the rule of the Dutch frequently packed up their farms and moved to new uncolonised areas. It was largely to escape oppression that the farmers trekked farther and farther from the seat of government.
The Trek Boers of the 19th century were the descendants of the early colonists. What they had learnt of government from the Dutch East India Company they carried into the wilderness with them. They were politically despotic and commercially monopolist justlike those they fled from.
The Dutch-descended colonists in the eastern and northeastern parts of the colony were not cultivators of the soil type farmers, but of purely pastoral and nomadic habits, ever ready to seek new pastures for their flocks and herds, and possessing no special affection for any particular area. These people, scattered over a wide territory, had lived for so long with little restraint from law.
In 1795 Holland had fallen under the influence of the French and its ruler the Prince of Orange was in exile in England, as such the British sought to secure the colony from Dutch/French Control. After several battles and skirmishes the Colony passed over into the control of the British. Although the overall governing of the colony significantly improved the Colonists resented these new laws. Britain was also going through major social and economical change with the drive to abolish Slavery. This same ideal was being pushed out into the colonies by missionaries much to the resentment of the local Boer population which ultimately culminated in the Boer Wars 1880-1881 and 1899-1902.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boer
| The 2nd Boer War was fought by British Empire against the Boers. The Boers were made up of the South African Republic and the Republic of the Orange Free State. The Boer's declared war on 11th October 1899 and the conflict ended on 31st May 1902. | 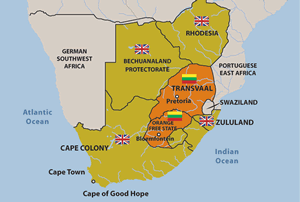 |

|
The conlfict was made up of 3 small phases or offensives:
Boer Offensive 1899. The Boer republican fighters were successful in three Battles. The invasion of northern Natal, Cape Colony and Mafeking. There were serious defeats for the British at Stormberg, Magersfontein and Colenso which became known as 'Black Week' (10th - 15th December 1899). British Counter Offensive 1900. With heavy reinforcements commanded by Lord Roberts with Lord Kitchener as his Chief of Staff, Imperial troops relieved the besieged towns of Ladysmith, Kimberley and Mafeking.Roberts then occupied Bloemfontein, the capital of the Orange Free State. British troops then entered Johannesburg and Pretoria was taken. ending the war with Roberts returning to England. |
| Guerrilla war offensive 1901. The Boers abandoned the British style of warfare and increased their reliance on small and mobile military units. In response, the British embarked on a scorched earth policy to deny supplies to the fighters. Farms were burnt movement was restricted miles of wire fencing was guarded by over 45,000 Soldiers. This operation produced large numbers of displaced Boer and African families. These refugees were sent to concentration camps around South Africa. These measures were largely responsible for bringing the Boers to the negotiation table to end the War in 1902. | |
| Boer War 1899-1902 | |
|---|---|
| Trooper Frederick Henderson Kirton | 5th Regiment Imperial Yeomanry |
| Captain William Basil Browell | Royal Field Artillery |
| Colour Sergeant John H Arthur Pickerell | 1st Battalion South Staffordshire Regiment |
| Lance Sergeant Fred Herbert Thubron | 5th Regiment Imperial Yeomanry |
| Sergeant John Gray Mark | 10th Prince of Wales Own Royal Hussars |
| Corporal Thomas Stafford | 1st Royal Welsh Fusilliers |
| Corporal Fredrick W Horn | 1st Durham Light Infantry |
| Private Philip Wood | 1st Durham Light Infantry |
| Trooper John Armstrong | 5th Imperial Yeomanry |
| Trooper William Holburn | 5th Regiment Imperial Yeomanry |
| Trooper Charles A Turnbull | 5th Regiment Imperial Yeomanry |
| Trooper Jacob Spain | 35th Battalion Imperial Yeomanry |
| Private Charles Thomas Haig | Royal Scots Greys |
| Trooper David James McClelland | 10th Prince of Wales Own Royal Hussars |